INDIAN ARMED FORCES CHIEFS ON
OUR RELENTLESS AND FOCUSED PUBLISHING EFFORTS

SP Guide Publications puts forth a well compiled articulation of issues, pursuits and accomplishments of the Indian Army, over the years

I am confident that SP Guide Publications would continue to inform, inspire and influence.

My compliments to SP Guide Publications for informative and credible reportage on contemporary aerospace issues over the past six decades.
Apache – A Versatile Machine
The Apache family of attack helicopters is widely accepted as the world’s most advanced, versatile and operationally proven multi-role, rotary-wing combat platform
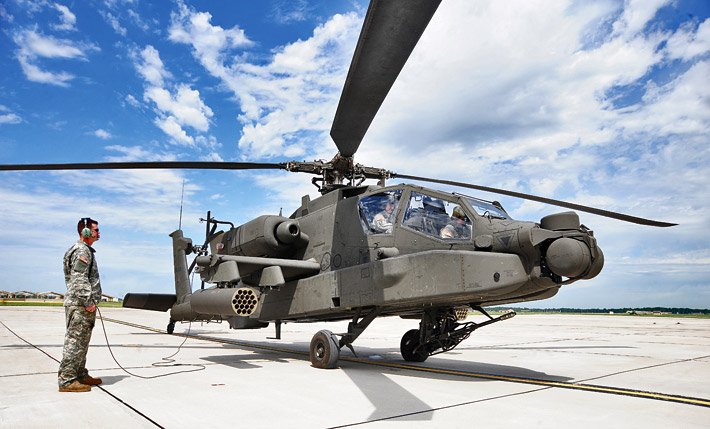

In August 2014, the Defence Acquisition Council (DAC) of the Ministry of Defence (MoD) finally cleared the proposal by the Indian Air Force (IAF) for the acquisition of 22 AH-64D Apache attack helicopters at a cost of $1.4 billion. The case for the acquisition of new and modern attack helicopters was initiated by the MoD in 2008. After a labyrinthine tendering process including rigorous evaluation by the IAF, the AH-64D Apache from the Boeing was selected from amongst the six platforms offered by global aerospace majors that were in the race for the contract. Competing with the AH-64D Apache were five other contenders, namely UH-60 Black Hawk from Sikorsky, the AH-1 Super Cobra from Bell Helicopter, the EC-665 Tiger from Eurocopter, the A-129 Mangusta from AgustaWestland and the Mil Mi-28 from Russia.
The AH-64D Apache was selected by the IAF from an array of highly successful models of rotary-wing platforms from the world’s leading manufacturers of attack helicopters. The contract with Boeing was signed in September 2015 with the delivery expected to commence after three years, i.e. in September 2018 and the last helicopter is scheduled to be delivered by March 2020. By the time the contract was signed, the AH-64D was replaced by the newer model, the AH-64E. The contract has an option for follow-on orders of another 11 of these attack helicopters. In any case, there is a proposal to acquire another 39 of these platforms for the Indian Army, taking the total induction of Apaches by the Indian armed forces to 61. Incidentally, the fuselage of the AH-64E Apache attack helicopter is to be manufactured by a joint venture (JV) company set up between Boeing and the Tata Group in Hyderabad. The first fuselage for the Apache made in India is expected to be delivered by 2018. The JV will be expected to build around 200 airframe structures for customers around the world as this Boeing-Tata JV will be the sole global supplier of fuselage for Apache attack helicopters.
“THE APACHE’S CAPABILITY SURPASSES PERFORMANCE LEVELS OF MILITARY COMBAT HELICOPTERS IN SERVICE OR ON THE DRAWING BOARD,” SAID JEFF KOHLER, VICE PRESIDENT, INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS DEVELOPMENT, BOEING DEFENSE, SPACE & SECURITY
The IAF has for some years been badly in need to augment if not totally replace its fleet of ageing Mi-25 and Mi-35 attack helicopters acquired from the Soviet Union over three decades ago. The IAF is now eagerly looking forward to inducting the latest model of the Apache attack helicopter designed, developed and manufactured by the US aerospace major Boeing Defense, Space & Security. These platforms will be armed with the latest and most potent weapon systems such as the AGM-114L-3 Hellfire Longbow missiles, AGM-114R-3 Hellfire-II missiles, Stinger Block I-92H missiles and 12 AN/APG-78 firecontrol radars among other assets. Equipped with an array of formidable capabilities by way of avionics and weapon systems, the fleet of 22 Apache AH-64E attack helicopters will enable the IAF to pack a far greater punch in the employment of its rotarywing fleet in the offensive role in the battlefield or against ground targets outside it.
The Apache — A Formidable Platform
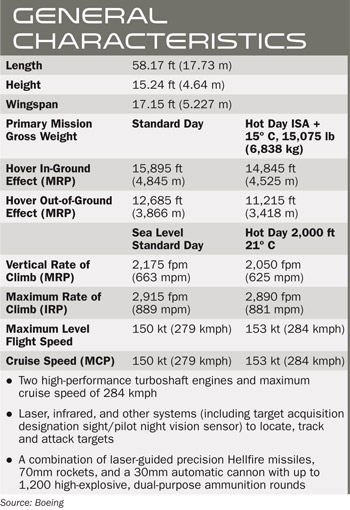
The Apache family of attack helicopters is widely accepted as the world’s most advanced and operationally proven, multirole, rotary-wing combat platform. Like several other US Army helicopters, this platform too has been named after an American Indian tribe, the Apache. The very name in this case suggests an aggressive spirit and confidence in the capabilities of the platform as also in its other attributes such as mobility, agility, flexibility, firepower and endurance. The Apache attack helicopter is a twin-engine, four-bladed platform that is operated by two pilots. As for its operational attributes, the Apache has a cruising speed of 284 kmph and has scored high ratings for its capability to carry heavy weapon loads and its exceptional ability to acquire both fixed and moving targets on the ground. Its several variants are currently in service with the US Army as also with the armed forces of as many as 116 countries across the globe. Some of the notable ones amongst the long list of operators of the Apache family of attack helicopters are Japan, Egypt, Greece, Israel, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, Taiwan, the United Arab Emirates, the Netherlands and the United Kingdom. The operators of this combat platform worldwide fly its three variants — the AH-64A Apache, the next-gen AH-64D Apache and the AH-64D Apache Longbow, which is equipped with the advanced Longbow fire control radar. At the MSPO Defence Exhibition in the city of Kielce in Poland in August 2015, Jeff Kohler, Vice President, International Business Development, Boeing Defense, Space & Security, stated, “The Apache’s capability surpasses the performance levels of any military combat helicopter in service or on the drawing board.”
Brief History of the Apache

In 1976, the US Army selected the AH-64 Apache over the YAH 63 fielded by Bell Helicopter. Hughes Helicopters were initially contracted by the US Government for production of the Apache. However, this company was taken over by McDonnell Douglas in 1984. The first AH-64D Apache Longbow, a substantially upgraded version of the original Apache, was delivered to the US Army in March 1997. Apache attack helicopters are now produced by the Boeing Defense, Space & Security. The Apache is also being produced under licence in the UK and is known as the AgustaWestland Apache. The Apaches have been employed by the US Army in the conflicts in Panama, Persian Gulf, Kosovo, Afghanistan and Iraq. Israel has also deployed the Apaches in military conflicts in Lebanon and the Gaza Strip.
The Apache Longbow is the only combat helicopter in service with the ability to rapidly detect, classify, prioritise and engage stationary or moving enemy targets at standoff ranges in all-weather conditions. The Apache Longbow’s advanced avionics suite gives combat pilots an unmatched advantage over enemy threats through the integration of the Longbow fire control radar, advanced Hellfire missiles, and an advanced avionics suite. The AH-64D Apache and the AH-64D Apache Longbow have numerous enhancements summarised as under:
- Enhanced accuracy of weapons at longer ranges.
- All-weather, day and night operations capability.
- Classification and threat-prioritisation of up to 128 targets in less than a minute.
- Integrated sensors, networking and digital communications for better situational awareness, management of the combat arena in real time and digital transmission of images and target locations to joint operations battlefield commanders.
The capabilities of the AH-64D Apache Longbow are significantly advanced over those of the AH-64A model. This was demonstrated by the original equipment manufacturer in tests and field trials by the US Army in the period 1996-96. The tests clearly demonstrated that the AH-64D Apache Longbow attack helicopters were 400 per cent more lethal, i.e. hitting more targets than the AH-64A which had already won the sobriquet of being the most capable and advanced attack helicopter in the world when it entered service. AH-64D Apache Longbow proved to have greater weapons accuracy at longer ranges and the ability to operate more effectively at night and in virtually any weather. The Apache Longbow’s advanced communications and combat capabilities, its ability to communicate digitally with other aircraft/ground forces and to share that information almost instantly, give the AH-64D a significant advantage over current combat helicopters and provides battlefield commanders the ability to more effectively manage the 21st century battlefield.
Currently, the US Army operates the AH-64E, the latest model of the Apache. The E model that is also known as Guardians, provides the US Army with the most advanced avionics and most powerful engines to date on the attack helicopter.





