INDIAN ARMED FORCES CHIEFS ON OUR RELENTLESS AND FOCUSED PUBLISHING EFFORTS

The insightful articles, inspiring narrations and analytical perspectives presented by the Editorial Team, establish an alluring connect with the reader. My compliments and best wishes to SP Guide Publications.

"Over the past 60 years, the growth of SP Guide Publications has mirrored the rising stature of Indian Navy. Its well-researched and informative magazines on Defence and Aerospace sector have served to shape an educated opinion of our military personnel, policy makers and the public alike. I wish SP's Publication team continued success, fair winds and following seas in all future endeavour!"

Since, its inception in 1964, SP Guide Publications has consistently demonstrated commitment to high-quality journalism in the aerospace and defence sectors, earning a well-deserved reputation as Asia's largest media house in this domain. I wish SP Guide Publications continued success in its pursuit of excellence.
PROBA-3 ESA Satellite Launch
ESA's PROBA-3 mission, launched by ISRO's PSLV-XL, aims to enhance solar research and space weather forecasting through artificial solar eclipses
 |
The Author is Former Director General of Information Systems and A Special Forces Veteran, Indian Army |
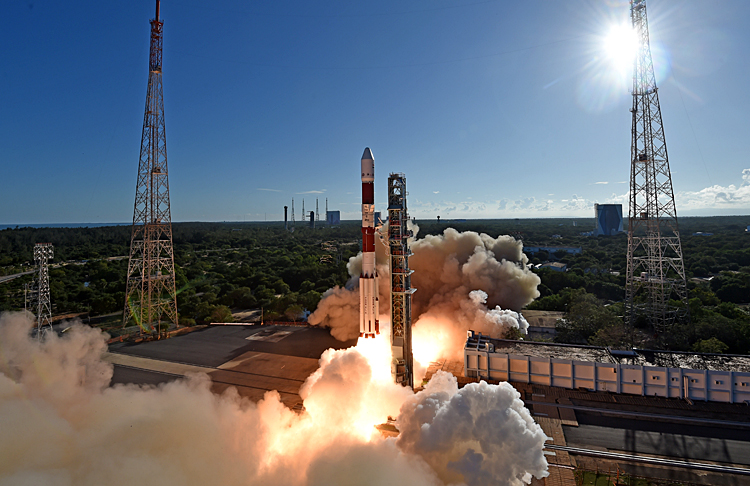

On December 5, 2024 the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) launched the European Space Agency's (ESA) PROBA-3 mission from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SHAR) in Sriharikota. This mission will utilize ISRO's PSLV-XL rocket to deploy two satellites into a highly elliptical orbit designed for studying the Sun's corona, the outer atmosphere of the Sun. The mission consists of two satellites: one, the 340-kg 'Coronagraph Spacecraft' housing the telescope for observing the corona; two, the 200-kg 'Occulter Spacecraft' to block direct sunlight and enable clear observations.
PROBA-3 is the world's first mission dedicated to precision formation flying, autonomously maintaining alignment within millimetres to simulate a large rigid structure in space
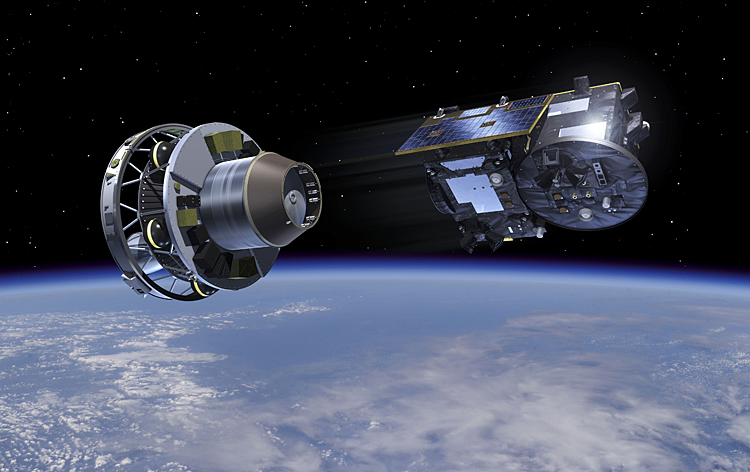
The primary goal of PROBA-3 is to observe the Sun's corona by creating an artificial solar eclipse through precision formation flying of two satellites. This method allows for continuous observation of solar phenomena, which is typically only possible during brief terrestrial total solar eclipses. The satellites will operate in an elliptical orbit ranging from 600 km to 60,000 km above Earth, with an orbital period of about 19.7 hours. They will maintain a precise alignment within millimetres to facilitate uninterrupted observations during their six-hour observation phase at peak altitude.
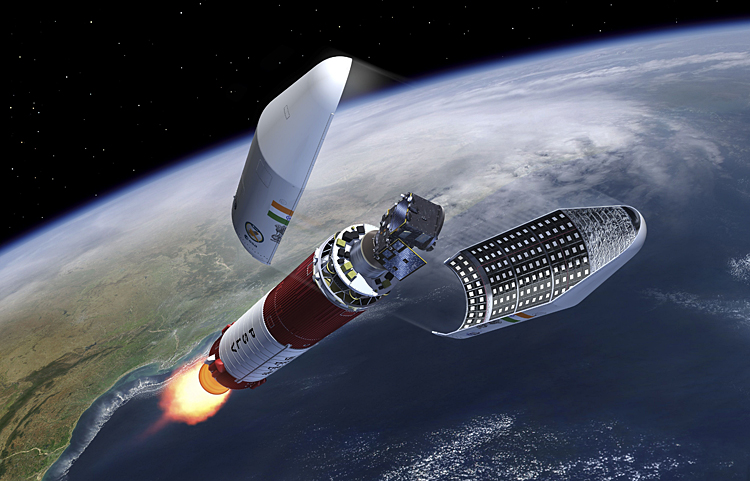
PROBA-3 is the world's first mission dedicated to precision formation flying. The satellites will autonomously maintain their formation, simulating a large rigid structure in space, crucial for achieving the mission's scientific objectives. This mission highlights growing collaboration between ESA and ISRO, marking ESA's first launch from India since 2001. It aims to enhance understanding of solar activities and improve space weather forecasting capabilities. The mission advancement in solar research and satellite technology, potentially paving the way for future multi-satellite missions and applications in space science.
The GSAT-20 satellite, exclusively using the advanced Ka-band frequency, marks ISRO's first heavy satellite launched by SpaceX into geosynchronous transfer orbit
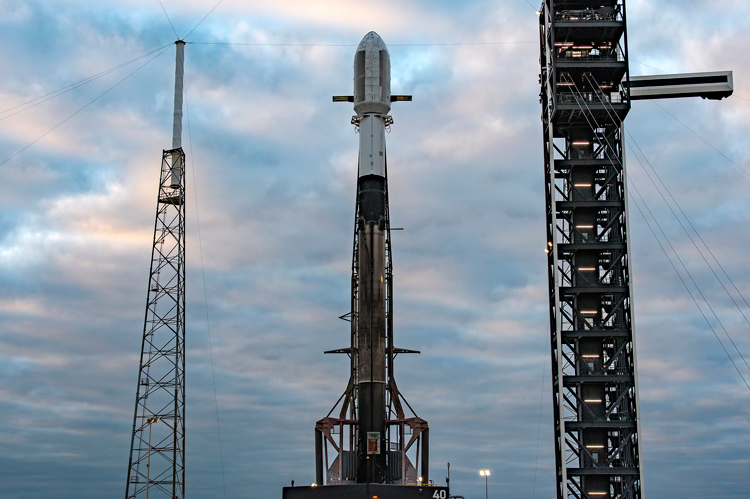
Earlier on November 18, ISRO's most advanced communications satellite GSAT-N2 (or GSAT-20) was launched by Elon Musk's SpaceX. The rocket used for the launch was the Falcon-9, placing the satellite in geosynchronous transfer orbit (GTO). GSAT-20 will provide broadband services in remote areas and in-flight Internet in passenger aircraft. The satellite is a project of New Space India Limited, ISRO's commercial arm. This is the first time ISRO has built a satellite that only uses the advanced Ka band frequency, a range of radio frequencies between 27 and 40 gigahertz (GHz), which enables the satellite to have higher bandwidth.

The GSAT-20 satellite, with a mission life of 14 years, will be in geostationary orbit 36,000 km about the Earth's surface. It is the first time ISRO used SpaceX's services for launching a heavy satellite into GTO. Earlier, ISRO had been using the services of the French company Ariane Space for launching such satellites. India required a heavy satellite launcher for scientific, commercial and strategic reasons. But ISRO had been facing challenges due to sanctions, particularly from the US, which prevented the transfer of critical cryogenic engine technology for launchers from Russia. It took ISRO a significant amount of time to indigenously operationalise this technology. Another crucial area for enhancing the GSLV (Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle) system is semi-cryogenic technology, which ISRO has been working on for several years.
ISRO has indigenously operationalised critical cryogenic engine technology after facing challenges due to US sanctions, marking a milestone for India's space programme."
Earlier on November 18, ISRO's most advanced communications satellite GSAT-N2 (or GSAT-20) was launched by Elon Musk's SpaceX. The rocket used for the launch was the Falcon-9, placing the satellite in geosynchronous transfer orbit (GTO). GSAT-20 will provide broadband services in remote areas and in-flight Internet in passenger aircraft. The satellite is a project of New Space India Limited, ISRO's commercial arm. This is the first time ISRO has built a satellite that only uses the advanced Ka band frequency, a range of radio frequencies between 27 and 40 gigahertz (GHz), which enables the satellite to have higher bandwidth.


The GSAT-20 satellite, with a mission life of 14 years, will be in geostationary orbit 36,000 km about the Earth's surface. It is the first time ISRO used SpaceX's services for launching a heavy satellite into GTO. Earlier, ISRO had been using the services of the French company Ariane Space for launching such satellites. India required a heavy satellite launcher for scientific, commercial and strategic reasons. But ISRO had been facing challenges due to sanctions, particularly from the US, which prevented the transfer of critical cryogenic engine technology for launchers from Russia. It took ISRO a significant amount of time to indigenously operationalise this technology. Another crucial area for enhancing the GSLV (Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle) system is semi-cryogenic technology, which ISRO has been working on for several years.
SpaceX is currently training Indian astronauts in preparation for the Gaganyaan mission, which aims to send Indian crew members to the International Space Station (ISS). This training is part of a collaborative effort involving NASA, SpaceX and ISRO. The astronauts began their intensive training at NASA's Johnson Space Centre in Houston in August 2024 and have also received hands-on experience at SpaceX's headquarters in Hawthorne, California.
The Gaganyaan mission, supported by training from NASA and SpaceX, represents India's entry into the elite group of nations capable of human spaceflight
The training includes familiarization with the Dragon spacecraft's systems, emergency protocols, and operational procedures. Astronauts have participated in simulations that cover docking and undocking manoeuvres, preparing them for real-time operations in space. The Gaganyaan mission represents a pivotal step for India as it aims to join the elite group of nations capable of human spaceflight, showcasing its growing ambitions in space exploration.

ISRO is presently also working on developing made-in-India car sensors to reduce the automotive industry's reliance on imported components. ISRO Chairman S Somanath speaking at the Bangalore Tech Summit on November 20 pointed out the contradiction in India's ability to manufacture high-quality sensors for rockets while the automotive sector remains dependent on imports for its sensor systems.
Somnath stressed that while India has successfully produced rocket sensors domestically, automotive sensors are still entirely imported. He expressed the need for collaboration between ISRO and the automotive industry to develop these sensors locally at a lower cost and in larger volumes. To facilitate this initiative, ISRO plans to organize workshops that will bring together industry stakeholders and experts from the space sector. The goal is to foster dialogue and collaboration to advance sensor technology development in India.





